Break-Even Point Calculator
What is the Break-Even Point?
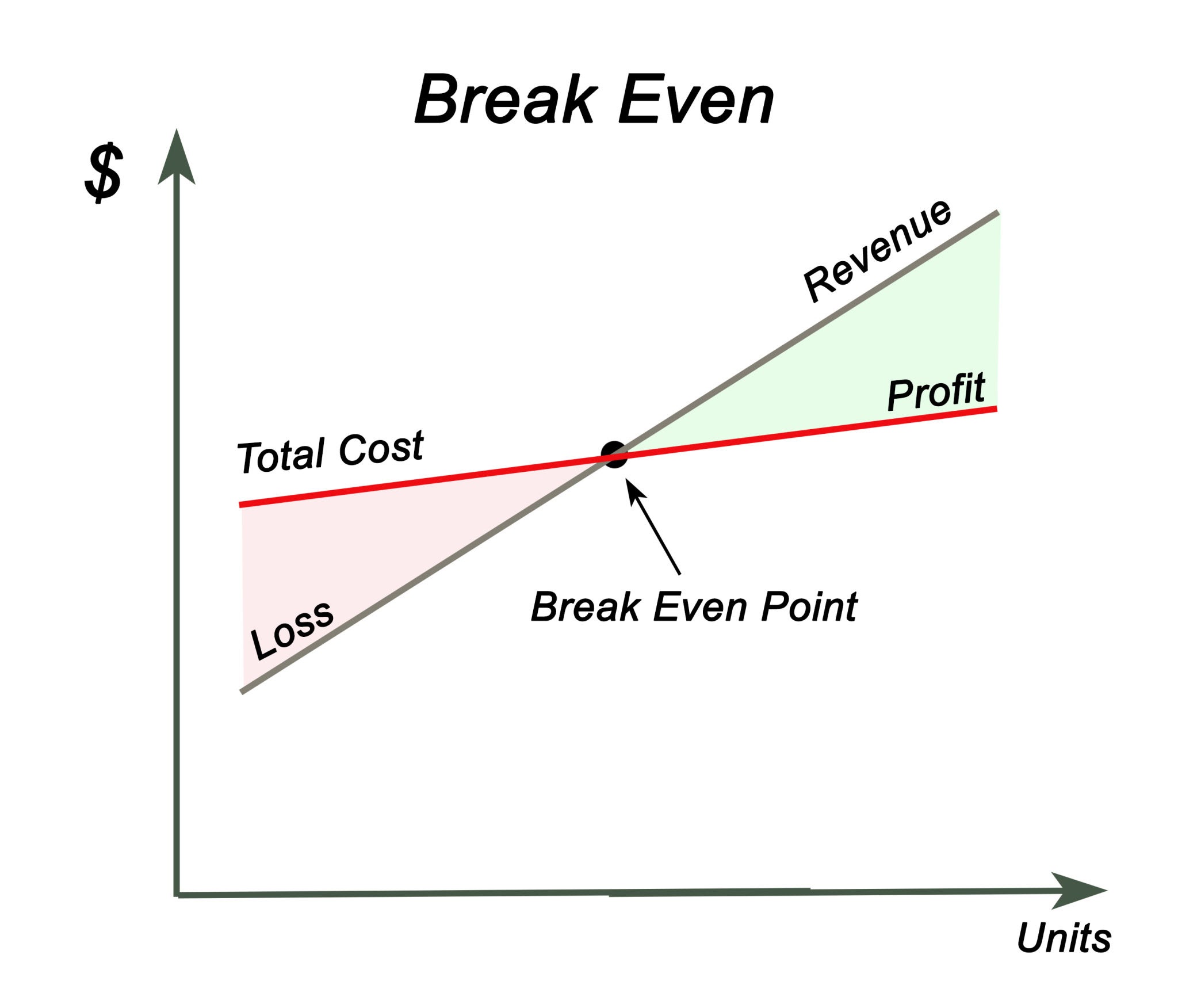
The Break-Even Point (BEP) is the precise milestone where your business stops losing money and starts making a profit.
It represents the sales volume at which your total revenues equal your total costs.
At this exact point, your net profit is zero. You haven’t made money yet, but you have successfully covered all your expenses.
Every single sale made after this point contributes directly to your profit.
Think of it as the “Survival Threshold”: Imagine you are filling a bucket with water (revenue). However, the bucket has holes in the bottom (costs). You need to pour water in fast enough to fill the bucket up to a specific line. Below that line, you are underwater. Above that line, you are profitable.
The Science Behind the Calculation
To understand how this calculator works, you need to understand the relationship between your fixed expenses and the profit you make on each individual item.
The calculator uses the standard Break-Even Formula:
Break-Even Point (Units) = (Total Fixed Costs)/(Price Per Unit - Variable Cost Per Unit)
Key Concepts:
- Fixed Costs: Expenses that remain the same regardless of how much you sell (e.g., rent, salaries, insurance).
- Variable Costs: Expenses that increase with every unit sold (e.g., raw materials, shipping, packaging).
- Contribution Margin: This is calculated as $(\text{Price} – \text{Variable Cost})$. It represents the portion of sales revenue that is not consumed by variable costs and is therefore available to cover fixed costs.
How to Use This Calculator
This tool is designed to give you a quick snapshot of your required sales volume. Follow these steps:
- Enter Fixed Costs (Total): Input your total monthly or annual overhead. Include rent, software subscriptions, and administrative salaries. Do not include costs that change based on production.
- Enter Price per Unit: Input the retail price at which you sell a single product or service.
- Enter Variable Cost per Unit: Input the direct cost to produce or deliver one single unit. This includes materials, labor for that specific unit, and shipping fees.
- Click Calculate: The tool will instantly determine how many units you need to move to cover your overhead.
Interpreting Your Results
Once you have your result, here is how to analyze the data:
- The “Units to Sell” Figure: This is your sales target. If the calculator says 500 units, and you currently only have the capacity to produce 300, you have a fundamental business model issue.
- The “Revenue Needed” Figure: This is the total cash flow required to stay afloat. It helps you verify if your market size is large enough to support your business.
What if my Break-Even Point is too high?
If the number seems unattainable, you have three “levers” you can pull:
- Raise your prices (Increases Contribution Margin).
- Lower your variable costs (Increases Contribution Margin).
- Cut your fixed costs (Lowers the threshold needed to cover overhead).
Limitations of This Model
While this calculator is a powerful planning tool, it does rely on a few assumptions:
- Linearity: It assumes that variable costs remain constant per unit. In reality, costs often go down as you scale up (bulk buying discounts), or up (overtime labor).
- Sales vs. Production: It assumes you sell everything you produce. It does not account for inventory that sits on a shelf unsold.
- Single Product Focus: This formula works best for businesses selling a single product or an “average” product. If you have a complex mix of products with vastly different margins, you may need to calculate a weighted average.
Other Financial Calculators / Articles :
- All Financial Calculators
- Compound Interest Calculator
- Net Present Value (NPV) Calculator
- Simple Interest Calculator
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR) Calculator
- Margin vs Markup Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Return on Investment (ROI) Calculator
- Depreciation Schedule Calculator
- WACC Calculator
- Bond Yield Calculator
- Discount Calculator
